Getting Started with RMF Demos using Docker
This article is aimed at providing its own standalone but supplementary information to existing documentations regarding Open Robotics’s Robot Middleware Framework (RMF).
While the documentation of RMF is comprehensive, readers or developers may still encounter confusion trying to getting an immediate first-hand experience on RMF and how it works by simply following it due to several ambiguous portion of Open Robotic’s instructions. Therefore, by writing this article, a relatively more fool-proof method of getting started with RMF Demos can be achieved for any new ROS 2 developers working with the award-winning open-source software.
Eg. In its suggestion for the use of
rocker(https://github.com/open-rmf/rmf), it did not specify what command to run to get any of the demos running while not worrying about adhering to necessary environment dependencies. As a result, readers like me are left wondering what other actions need to be taken to simply get started. Furthermore, the instructions to get started using DOcker has the codebase running headless without graphical form which defeats the purpose of getting started and understanding when none can be visualised by anyone following the document.
Steps
1. Download the latest docker image containing the RMF demos:
docker pull cardboardcode/rmf_demos:humble
Caution: This instruction will take a while depending on your internet and local workstation. Grab a coffee or do something else while you wait.
2. Rename the docker image to rmf:latest:
docker tag cardboardcode/rmf_demos:humble rmf:latest
3. Enable Graphic User Interface access for docker:
xhost +local:docker
Note that this command runs a security risk and should not be used as an official deployment. For the context of research and learning, this command should be okay.
4. Launch rmf_demos_gz_classic ROS 2 package:
docker run -it --rm \
--name ros2_rmf \
-e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
-v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
--net=host \
rmf:latest /bin/bash -c "ros2 launch rmf_demos_gz_classic hotel.launch.xml"
If a GPU (Graphical Processing Unit) is available, you can run the following command instead:
docker run -it --rm \
--name ros2_rmf \
--runtime=nvidia \
-e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
-v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
--net=host \
rmf:latest /bin/bash -c "ros2 launch rmf_demos_gz_classic hotel.launch.xml"
6. Run rmf_dashboard using the command below:
docker run -it --rm \
--name rmf_web_dashboard_demo_c \
-p 3000:80 \
ghcr.io/open-rmf/rmf_deployment_template/rmf-web-dashboard-local:humble
7. Run rmf_api_server using the command below:
docker run -it --rm \
--name rmf_web_rmf_server_demo_c \
--net=host \
ghcr.io/open-rmf/rmf_deployment_template/rmf-web-rmf-server:humble
8. Open the following link in your browser to access the RMF Panel which you can use to send requests to robots in simulation:
Link: http://localhost:3000/dashboard
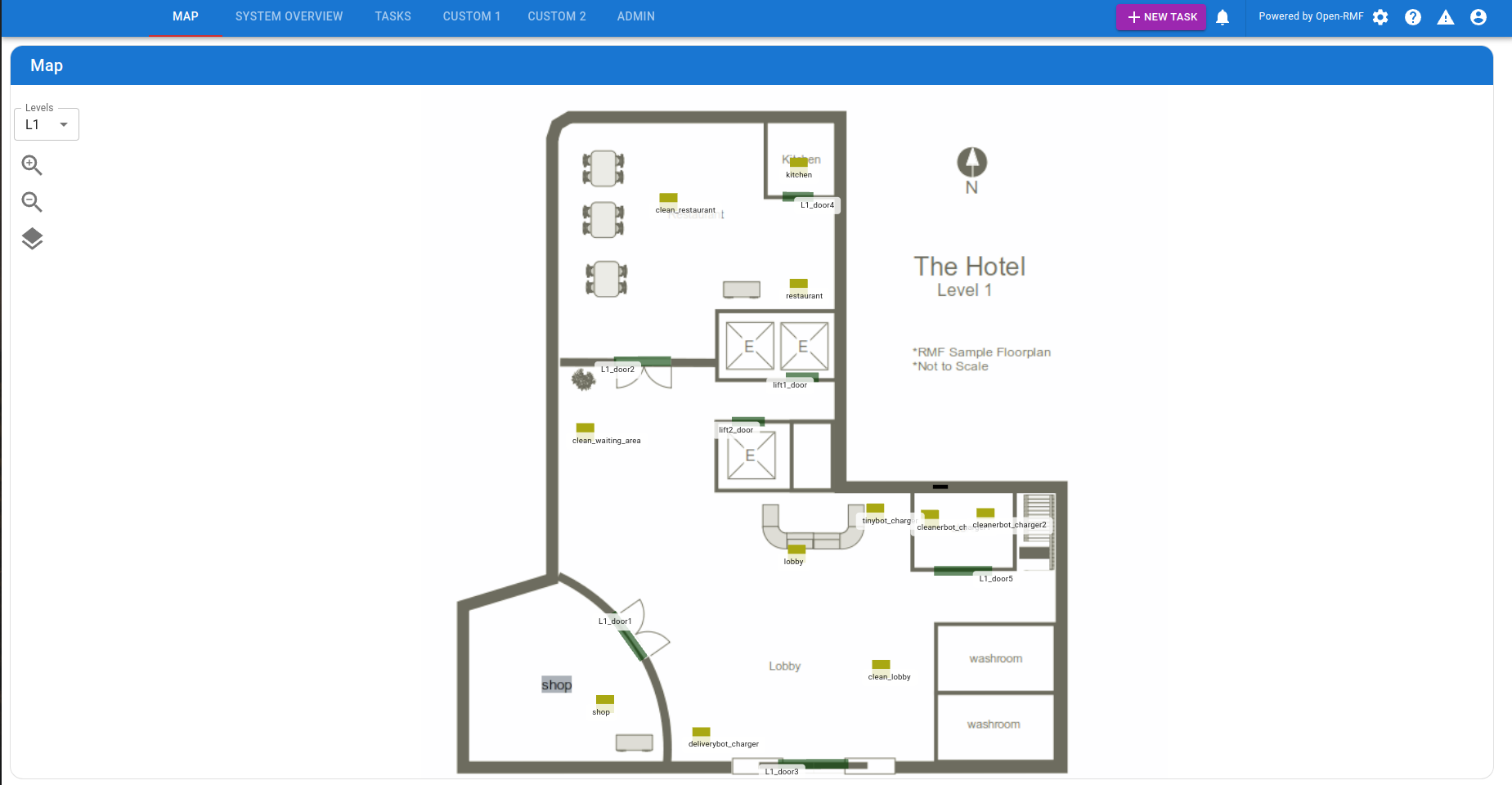
Verify ✅
1. Run RMF Patrol and Clean tasks using the commands below:
docker exec -it ros2_rmf bash -c "source /ros_entrypoint.sh && ros2 run rmf_demos_tasks dispatch_patrol -p restaurant L3_master_suite -n 1 --use_sim_time"
docker exec -it ros2_rmf bash -c "source /ros_entrypoint.sh && ros2 run rmf_demos_tasks dispatch_clean -cs clean_lobby --use_sim_time"
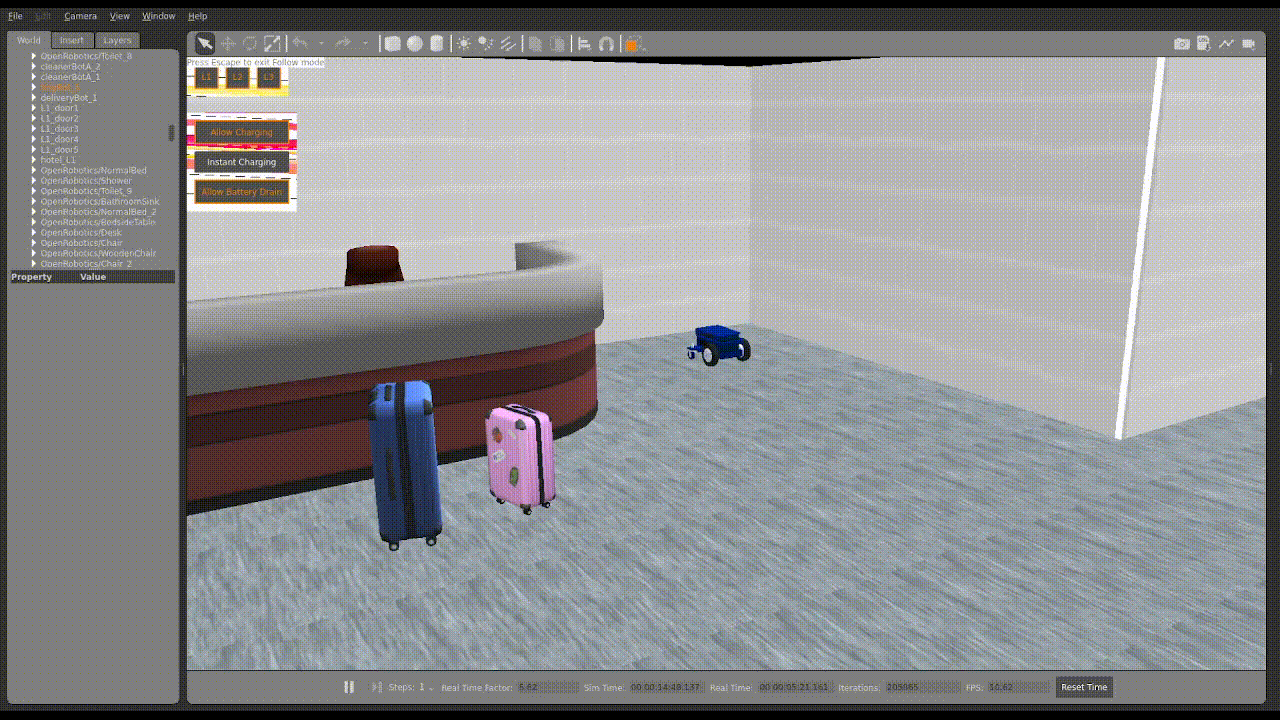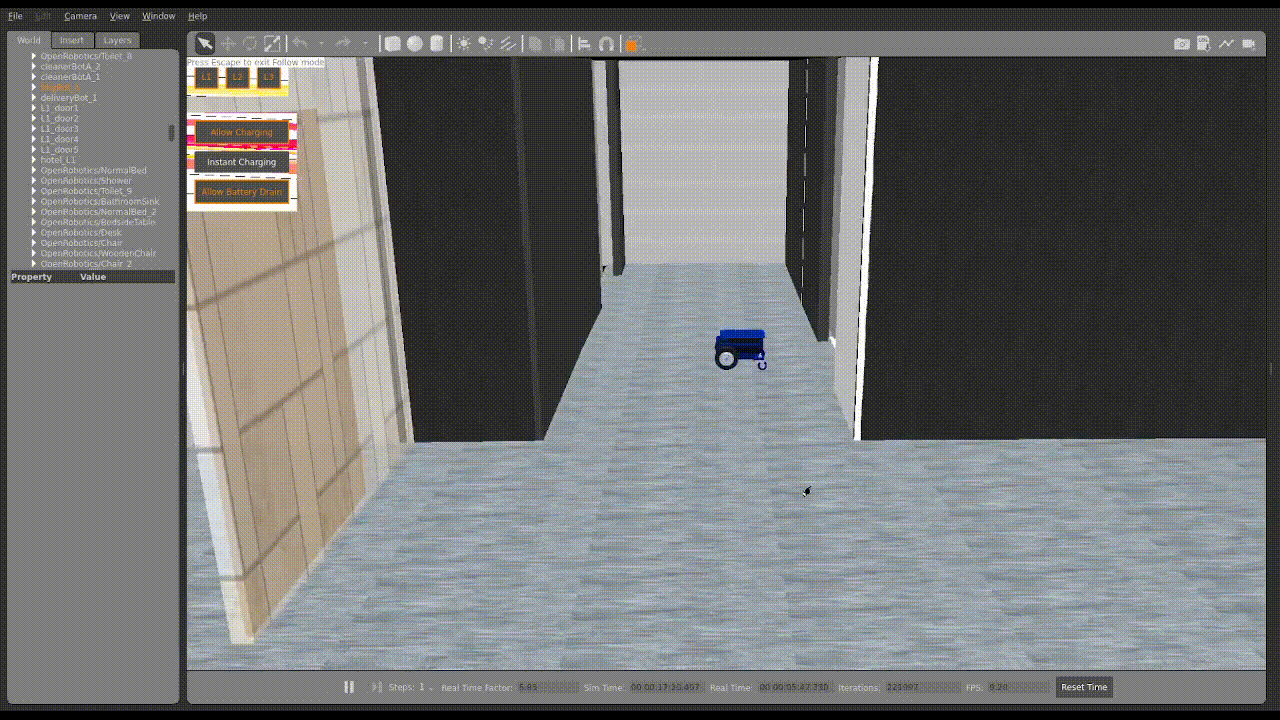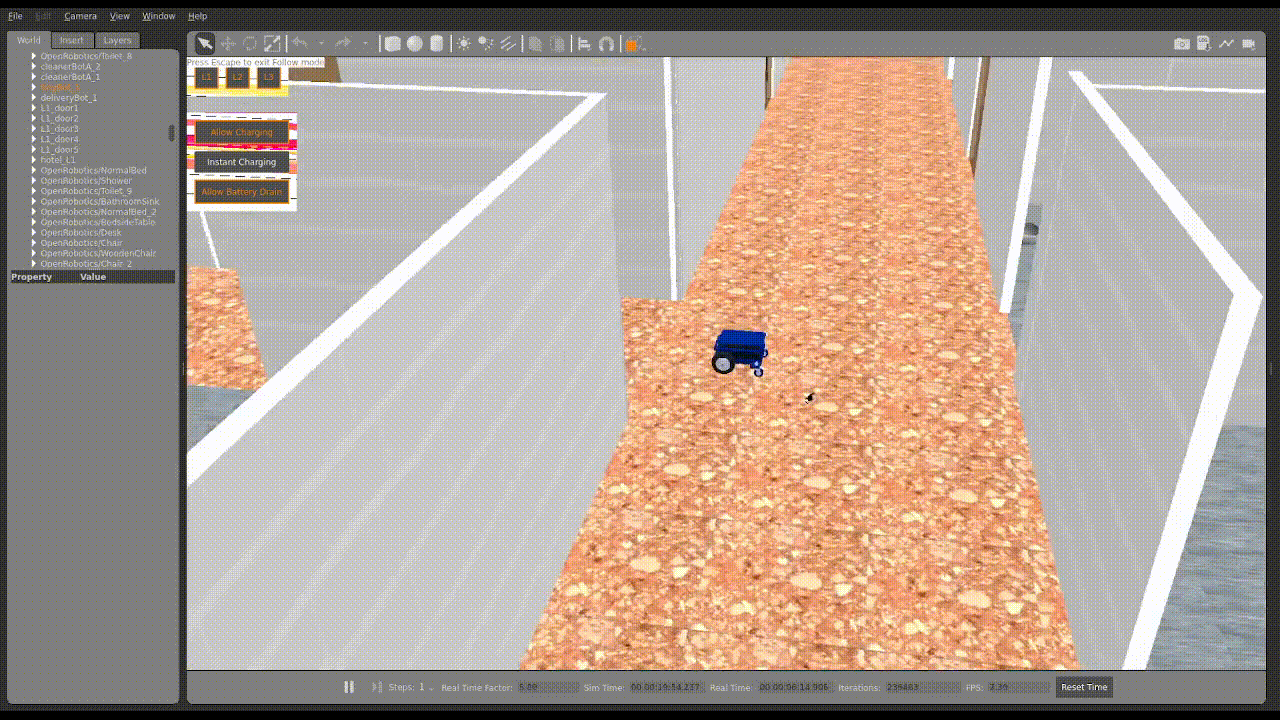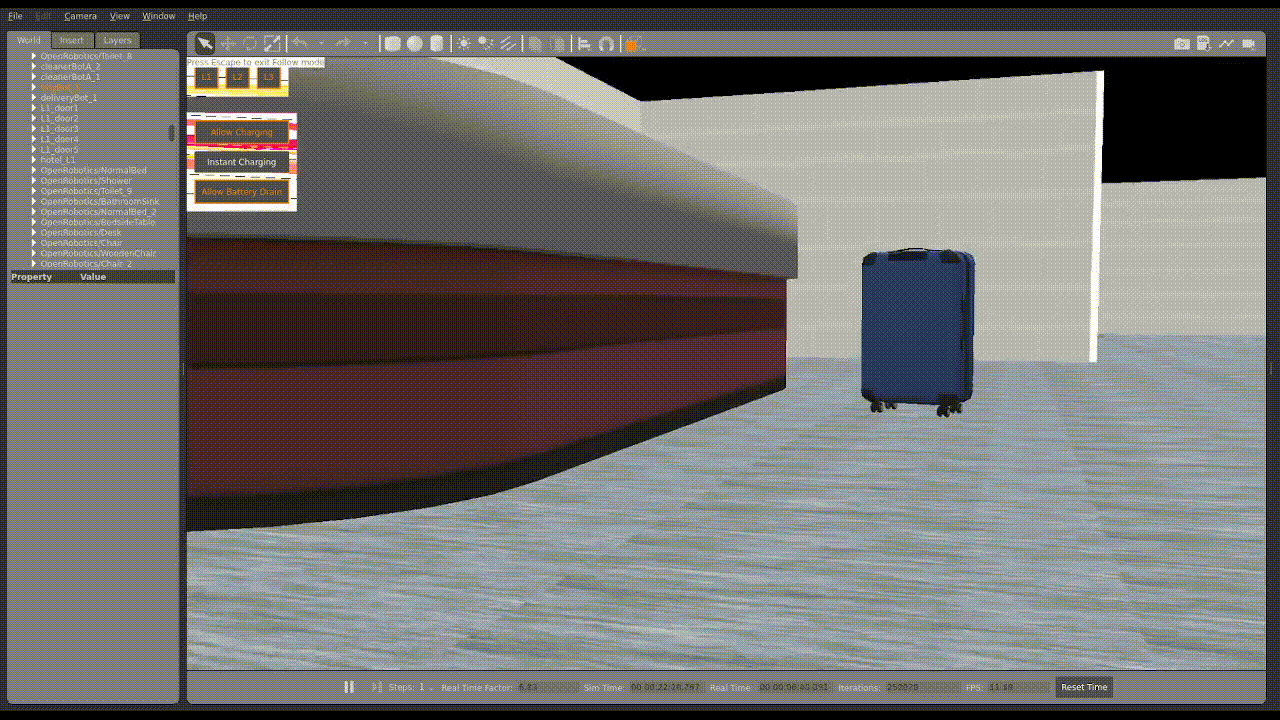
2. Upon uploading, you should then see the robots moving in Gazebo similar to what is shown below.